SharePoint Framework – Implementing Separation of concerns (SoC)
Overview
SharePoint Framework client web parts are developed using TypeScript and any supporting JavaScript framework (for e.g. React, Angular, KnockOut, etc.). The SPFx solution provides basic structure to start developing. However we can take one step further to implement best practices.
In this article, we will explore how we can implement Separation of Concerns (SoC) principle in a SharePoint Framework solution.
Separation of Concerns (SoC) Overview
Separation of Concerns is a design principle for separating our program (or solution) into distinct section. Where in each section addresses a separate concern.
A code is split into sections with each responsible for its own functionality (e.g. business logic, presentation logic, user interface, etc.).

Each section is independent and does not need to know internals of other section. They only need to know how to communicate with each other by passing certain information and get the desired result.
Advantages:
- Each section is easier to maintain
- Each section can be easily unit tested
- Each section can be rewritten, if needed without affecting other sections
In SPFx solution, we can refer each section as a Service.
Build SoC Scenario
In this article, we will reuse React Based OrgChart implemented in the previous article. Download the source code from previous article to get started with implementing SoC.
The React component OrgChartViewer.tsx at “\src\webparts\orgChartViewer\components" has all the data access, business and presentation logic. We will start implementing by services to develop an independent sections.
An OrgChartService class
- Under src, create a folder services.
-
Add a file OrgChartService.ts file under it.
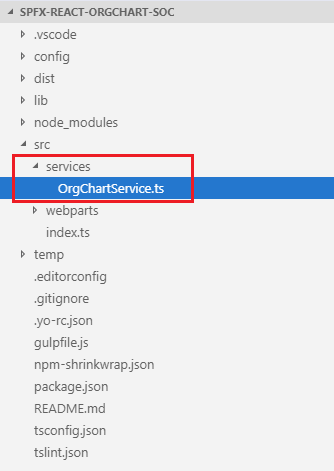
- We will move all data related methods from UI to this service class.
- Also declare public interface of the service.
IDataService.ts
import { IOrgChartItem, ChartItem } from './IOrgChartItem';
export interface IDataService {
getOrgChartInfo: (listName?: string) => Promise<any>;
}
OrgChartService.ts
import { ServiceScope, ServiceKey } from "@microsoft/sp-core-library";
import { IOrgChartItem, ChartItem } from './IOrgChartItem';
import { IDataService } from './IDataService';
import { SPHttpClient, SPHttpClientResponse } from '@microsoft/sp-http';
import { PageContext } from '@microsoft/sp-page-context';
export class OrgChartService implements IDataService {
public static readonly serviceKey: ServiceKey<IDataService> = ServiceKey.create<IDataService>('orgChart:data-service', OrgChartService);
private _spHttpClient: SPHttpClient;
private _pageContext: PageContext;
private _currentWebUrl: string;
constructor(serviceScope: ServiceScope) {
serviceScope.whenFinished(() => {
// Configure the required dependencies
this._spHttpClient = serviceScope.consume(SPHttpClient.serviceKey);
this._pageContext = serviceScope.consume(PageContext.serviceKey);
this._currentWebUrl = this._pageContext.web.absoluteUrl;
});
}
public getOrgChartInfo(listName?: string): Promise<IOrgChartItem[]> {
return new Promise<IOrgChartItem[]>((resolve: (itemId: IOrgChartItem[]) => void, reject: (error: any) => void): void => {
this.readOrgChartItems(listName)
.then((orgChartItems: IOrgChartItem[]): void => {
resolve(this.processOrgChartItems(orgChartItems));
});
});
}
private readOrgChartItems(listName: string): Promise<IOrgChartItem[]> {
return new Promise<IOrgChartItem[]>((resolve: (itemId: IOrgChartItem[]) => void, reject: (error: any) => void): void => {
this._spHttpClient.get(`${this._currentWebUrl}/_api/web/lists/getbytitle('${listName}')/items?$select=Title,Id,URL,Parent/Id,Parent/Title&$expand=Parent/Id&$orderby=Parent/Id asc`,
SPHttpClient.configurations.v1,
{
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json;odata=nometadata',
'odata-version': ''
}
})
.then((response: SPHttpClientResponse): Promise<{ value: IOrgChartItem[] }> => {
return response.json();
})
.then((response: { value: IOrgChartItem[] }): void => {
resolve(response.value);
}, (error: any): void => {
reject(error);
});
});
}
private processOrgChartItems(orgChartItems: IOrgChartItem[]): any {
let orgChartNodes: Array<ChartItem> = [];
var count: number;
for (count = 0; count < orgChartItems.length; count++) {
orgChartNodes.push(new ChartItem(orgChartItems[count].Id, orgChartItems[count].Title, orgChartItems[count].Url, orgChartItems[count].Parent ? orgChartItems[count].Parent.Id : undefined));
}
var arrayToTree: any = require('array-to-tree');
var orgChartHierarchyNodes: any = arrayToTree(orgChartNodes);
var output: any = JSON.stringify(orgChartHierarchyNodes[0]);
return JSON.parse(output);
}
}
What is ServiceKey and ServiceScope?
These classes allows to implement dependency injection. Instead of passing reference to single dependency, we can pass scope as an argument to section and section calls consume() method to call the needed service.
The below line of code declares the service key:
public static readonly serviceKey: ServiceKey<IOrgChartItem> = ServiceKey.create<IOrgChartItem>('orgChart:data-service', OrgChartService);
The key will help to identify service within the scope. To ensure default implementation always exists, it is better to always call consume() inside a callback from serviceScope.whenFinished().
Implement Mock Data Service
When the web part is running on local SharePoint workbench, mock data service can provide the mock data to web part.
Add MockDataService.ts file under “\src\services” folder.
import { ServiceScope, ServiceKey } from "@microsoft/sp-core-library";
import { IDataService } from './IDataService';
export class MockDataService implements IDataService {
public static readonly serviceKey: ServiceKey<IDataService> = ServiceKey.create<IDataService>('orgChart:mock-service', MockDataService);
constructor(serviceScope: ServiceScope) {
}
public getOrgChartInfo(): Promise<any> {
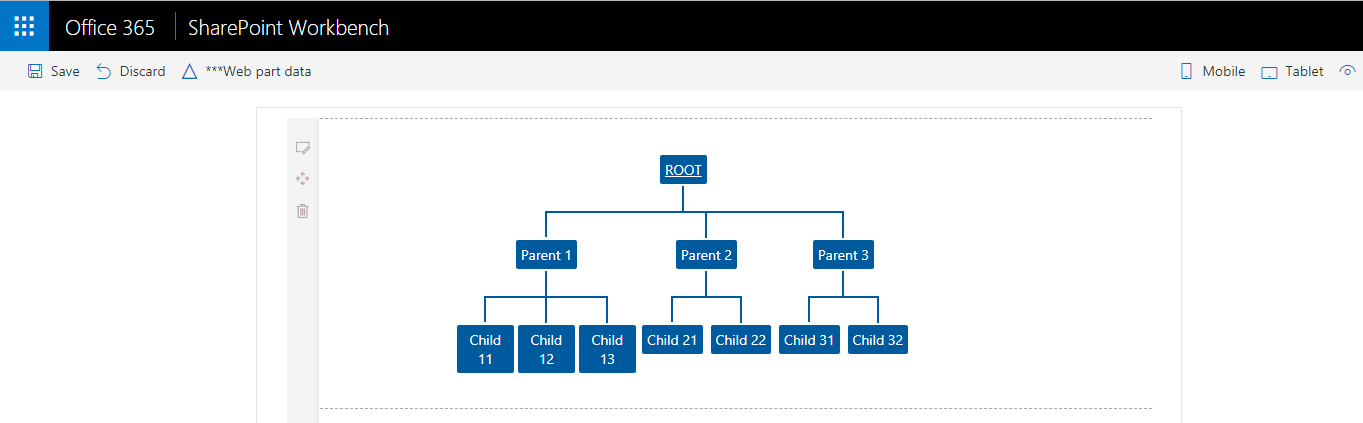
const initechOrg: any =
{
id: 1,
title: "ROOT",
url: {Description: "Microsoft", Url: "http://www.microsoft.com"},
children:[
{
id: 2,
title: "Parent 1",
url: null,
parent_id: 1,
children:[
{ id: 3, title: "Child 11", parent_id: 2, url: null },
{ id: 5, title: "Child 12", parent_id: 2, url: null },
{ id: 6, title: "Child 13", parent_id: 2, url: null }
]
},
{
id: 7,
title: "Parent 2",
url: null,
parent_id: 1,
children:[
{ id: 8, title: "Child 21", parent_id: 7, url: null },
{ id: 9, title: "Child 22", parent_id: 7, url: null }
]
},
{
id: 10,
title: "Parent 3",
url: null,
parent_id: 1,
children:[
{ id: 11, title: "Child 31", parent_id: 10, url: null },
{ id: 12, title: "Child 32", parent_id: 10, url: null }
]
}
]
};
return new Promise<any>((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(initechOrg)));
});
}
}
Update WebPart class to consume Service
- Open web part class OrgChartViewer.tsx under “\src\webparts\orgChartViewer\components".
- Update the class to consume the implemented service.
import * as React from 'react';
import styles from './OrgChartViewer.module.scss';
import { IOrgChartViewerProps } from './IOrgChartViewerProps';
import { IOrgChartViewerState } from './IOrgChartViewerState';
import { IOrgChartItem, ChartItem } from '../../../services/IOrgChartItem';
import { IDataNode, OrgChartNode } from './OrgChartNode';
import { SPHttpClient, SPHttpClientResponse } from '@microsoft/sp-http';
import { escape } from '@microsoft/sp-lodash-subset';
import { ServiceScope, Environment, EnvironmentType } from '@microsoft/sp-core-library';
import { OrgChartService } from '../../../services/OrgChartService';
import { MockDataService } from '../../../services/MockDataService';
import { IDataService } from '../../../services/IDataService';
import OrgChart from 'react-orgchart';
export default class OrgChartViewer extends React.Component<IOrgChartViewerProps, IOrgChartViewerState> {
private dataCenterServiceInstance: IDataService;
constructor(props: IOrgChartViewerProps, state: IOrgChartViewerState) {
super(props);
this.state = {
orgChartItems: []
};
let serviceScope: ServiceScope = this.props.serviceScope;
switch (Environment.type) {
case EnvironmentType.SharePoint:
case EnvironmentType.ClassicSharePoint:
// Based on the type of environment, return the correct instance of the IDataCenterService interface
// Mapping to be used when webpart runs in SharePoint.
this.dataCenterServiceInstance = serviceScope.consume(OrgChartService.serviceKey);
this.dataCenterServiceInstance.getOrgChartInfo(this.props.listName).then((orgChartItems: any) => {
this.setState({
orgChartItems: orgChartItems
});
});
break;
// case EnvironmentType.Local:
// case EnvironmentType.Test:
default:
// Webpart is running in the local workbench or from a unit test.
this.dataCenterServiceInstance = serviceScope.consume(MockDataService.serviceKey);
this.dataCenterServiceInstance.getOrgChartInfo().then((orgChartItems: any) => {
this.setState({
orgChartItems: orgChartItems
});
});
}
}
public render(): React.ReactElement<IOrgChartViewerProps> {
return (
<div className={ styles.orgChartViewer }>
<div className={ styles.container }>
<div className={ styles.row }>
<div className={ styles.column }>
<OrgChart tree={this.state.orgChartItems} NodeComponent={this.MyNodeComponent} />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
private MyNodeComponent = ({ node }) => {
if (node.url) {
return (
<div className="initechNode">
<a href={ node.url.Url } className={styles.link} >{ node.title }</a>
</div>
);
}
else {
return (
<div className="initechNode">{ node.title }</div>
);
}
}
}
Test the WebPart
- On the command prompt, type
gulp serve. - Open SharePoint site.
- Navigate to /_layouts/15/workbench.aspx
- Add the webpart to page.
-
Edit the webpart and add list name (i.e. OrgChart) to web part property.
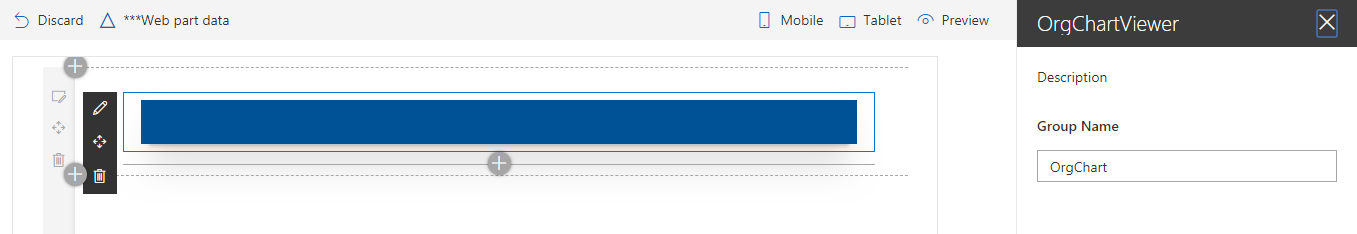
-
The web part should display the data from SharePoint list in an organization chart
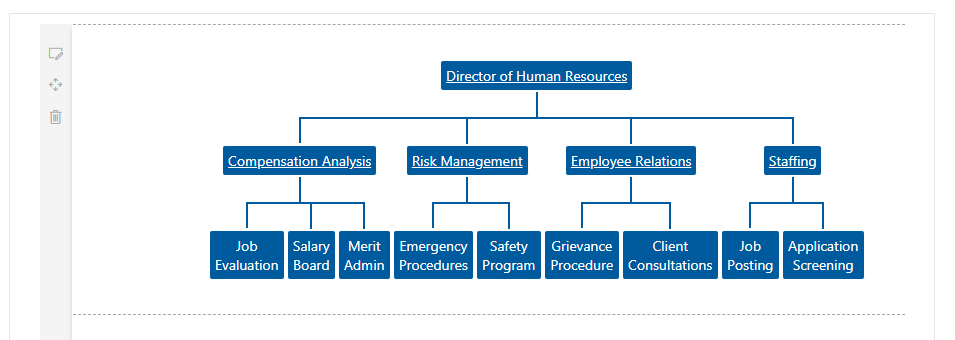
- Click on the nodes with url to see test the page navigation.
- Open Local SharePoint workbench (https://localhost:4321/temp/workbench.html)
-
Add the webpart to page.
Summary
With the implementation of Separation of concerns (SoC) all sections are separated. Code is easier to maintain and upgrade without touching other sections. ServiceScope helps to build SoC in SharePoint Framework solutions.
This content was originally posted here.


Leave a comment