SPFx Avoid NPM Package Dependencies
Overview
NPM (Node Package Manager) is a package manager for JavaScript as like Nuget for managed code of .Net framework. NPM is used to consume third party libraries in SharePoint Framework (SPFx) solutions. All of the required packages like jQuery, React, Angular, Office Fabric UI, etc. can be added to the solution using NPM. The packages are dependent on each other. Change of semantic versioning (semver) of one package can break the dependency build toolchain.
In this article, we will understand the package dependencies and how it can be avoided.
Semantic Versioning
Each package has a version associated with it which is denoted by 3 numbers (major.minor.patch)
- Major represents substantial changes to package that may break the existing code.
- Minor represents non-breaking changes.
- Patch represents no interface changes.
The dependencies in SPFx solutions are recorded in package.json in following ways:
Caret dependency:
- Any version up to (but not including) is accepted
- Example: ^2.3.1 means greater than or equal to 2.3.1 but less than 3.0.0
Tilde dependency:
- It is similar to Caret dependency, but the range is narrower
- Example: ~2.3.1 means greater than or equal to 2.3.1 but less than 2.4.0
Exact dependency:
- Constrained to a specific version
- Example: 2.3.1 means 2.3.1 only
Lock Down the Package version
When a package is added to SPFx solution using npm install command, the package is downloaded and installed to the solution. It can be found under node\modules folder and entry of it is recorded in package.json file. Adding --save flag to npm install command ensure that the dependency is recorded to package.json. This means, whenever any developer runs npm install or npm update on the SPFx solution, NPM will download package of appropriate version. It is always recommended to specify --save or --save-exact while running npm install command to record and track the dependencies.
Failing to specify --save flag will not record the entry in package.json and can cause code to fail because of missing packages. TypeScript compiler might throw an error Cannot find module.
node_modules folder contains tree of dependencies for packages. First level of dependencies are stored in child node_modules folders. Because of this reason, node_modules folder can grow bigger in size and deep in hierarchy.
--save-exact will avoid caret or tilde dependencies only at first level, which makes difficult to get the exact build unless we check-in entire node_modules folder to source control (which is not recommended and feasible solution).
Freeze the entire tree of dependencies
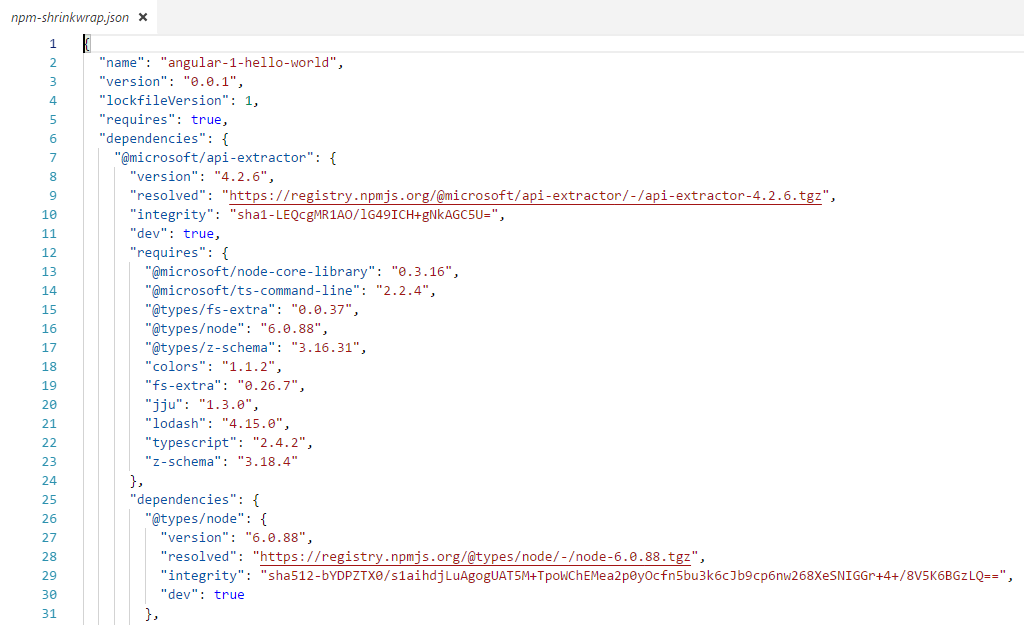
npm shrinkwrap command will help you to freeze the entire tree of dependencies. It creates a JSON file called npm-shrinkwrap.json which records exact version of each package used in the solution. It is important in the production environment that same versions of packages get installed as that used during development.

Because of using npm shrinkwrap, if npm install or npm update commands are used against the solution containing npm-shrinkwrap.json will restore the exact version of packages and avoids code break issues for other developers.
Updating npm-shrinkwrap.json file
npm-shrinkwrap.json file freezes the version of package. However, we might have to update any single version of the package in future.
To update single package version run below command:
npm update <package_name>
This will only update a single package. Once done re-run npm shrinkwrap command to update npm-shrinkwrap.json file.
To find out the outdated packages in the solution, run below command:
npm outdated
Summary
It is recommended to run npm shrinkwrap every time against the SPFx solution before you release the version of your solution. It will record exact version of package dependencies. Also ensure to check-in the npm-shrinkwrap.json file to source control. This will allow to rebuild your solution on any machine even though newer versions of used packages are released in the future.
This content was originally posted here.


Leave a comment