Running Your First Agent using Microsoft Agent Framework

Introduction
The Microsoft Agent Framework is a developer toolkit that allows you to build, orchestrate, and run intelligent agents that can think, reason, and take actions. These agents can perform specific tasks, call APIs, or integrate with real-world systems.
In this article, we’ll learn how to run your first agent using Microsoft’s Agent Framework - both in Python and C#. Instead of simply greeting users, our sample agents will help users track daily tasks in a simple and interactive way.
Understanding the Microsoft Agent Framework
At its core, the Agent Framework enables developers to:
- Create autonomous agents that use AI reasoning.
- Integrate with custom tools (functions, APIs, data sources).
- Run locally or in the cloud using simple commands.
- Extend agents with plugins or external connectors.
The agent runtime handles the conversation loop — interpreting user input, reasoning about it, and taking the right actions (like calling a function or returning a message).
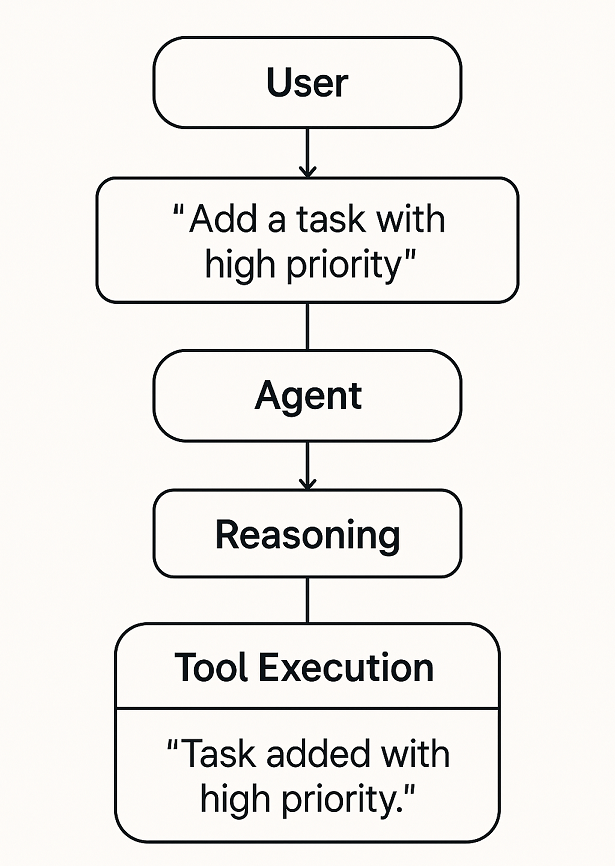
Example 1: Running an Agent in Python
Step 1: Prerequisites
Ensure you have:
- Python 3.10+
-
agentframework library installed via pip:
pip install agentframework
Step 2: Create the Agent File
Let’s create a Python agent called task_agent.py:
from agentframework import Agent
# Define the agent
agent = Agent(
name="task-agent",
instructions="You are a helpful assistant that helps users manage their daily tasks."
)
# Define a custom tool
@agent.tool
def add_task(task_name: str, priority: str = "normal"):
"""Add a new task with an optional priority."""
return f"✅ Task '{task_name}' added successfully with {priority} priority."
# Run the agent
if __name__ == "__main__":
agent.run()
Step 3: Run the Agent
In the terminal, execute:
python -m agentframework run task_agent.py
You will enter an interactive shell where you can talk to the agent.
Example conversation:
> Add a task to review the AI presentation with high priority
✅ Task 'review the AI presentation' added successfully with high priority.
Example 2: Running an Agent in C#
Step 1: Setup Project
Create a new .NET console project:
dotnet new console -n TaskAgentApp
cd TaskAgentApp
dotnet add package Microsoft.AgentFramework
Step 2: Create the Agent Class
In Program.cs, define and run your agent:
using Microsoft.AgentFramework;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
var agent = new Agent(
name: "task-agent",
instructions: "You are an intelligent assistant that helps users plan their daily schedule."
);
// Define a simple tool
agent.AddTool("create_task", (parameters) =>
{
string title = parameters["title"].ToString();
string time = parameters.ContainsKey("time") ? parameters["time"].ToString() : "unspecified time";
return $"🗓️ Task '{title}' scheduled for {time}.";
});
// Run the agent
agent.Run();
}
}
Step 3: Run the Application
Run the following command:
dotnet run
Sample interaction:
> Create a task to call the client at 3 PM
🗓️ Task 'call the client' scheduled for 3 PM.
Use Cases
The Microsoft Agent Framework can be extended to fit various business and productivity needs:
| **Use Case ** | Description |
|---|---|
| Personal Productivity | Build agents to manage schedules, tasks, or reminders. |
| Customer Support | Create agents that handle FAQs or escalate complex queries. |
| Business Workflows | Automate tasks like report generation, ticket updates, or approvals. |
| Data Insights | Connect to enterprise data sources for intelligent analysis and suggestions. |
| Copilot Integrations | Extend Copilot scenarios by embedding agents with custom logic or memory. |
Summary
In this article, we explored how to run your first Microsoft Agent Framework agent using both Python and C#.
We created simple task management agents that respond to user commands using natural language. The framework abstracts the complexity of reasoning and orchestration, allowing developers to focus on defining tools and business logic.


Leave a comment