SharePoint Framework – Multilingual Support (Localization)
Overview
SharePoint has supported localization in each of its version to help build better content for users worldwide. SharePoint Framework is also not an exception to it. SPFx offers multilingual support with the help of localized resource files as a part of SPFx solution.
In this article, we will explore localization options with SPFx. We will use React JS to develop the example.
Create SPFx Solution
-
Open command prompt. Create a directory for SPFx solution.
md spfx-react-localization -
Navigate to above created directory.
cd spfx-react-localization -
Run Yeoman SharePoint Generator to create the solution.
yo @microsoft/sharepoint -
Yeoman generator will present you with the wizard by asking questions about the solution to be created.
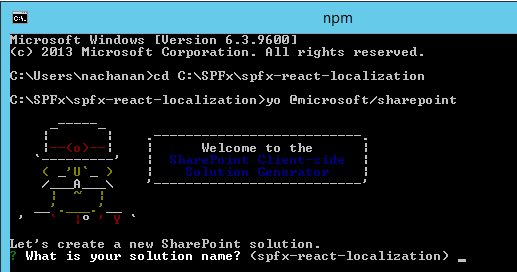
- Solution Name: Hit enter to have default name (spfx-react- localization in this case) or type in any other name for your solution.
- Selected choice: Hit enter
- Target for component: Here we can select the target environment where we are planning to deploy the client webpart i.e. SharePoint Online or SharePoint OnPremise (SharePoint 2016 onwards).
- Selected choice: SharePoint Online only (latest)
- Place of files: We may choose to use the same folder or create a subfolder for our solution.
- Selected choice: Same folder
- Deployment option: Selecting Y will allow the app to deployed instantly to all sites and will be accessible everywhere.
- Selected choice: N (install on each site explicitly)
- Type of client-side component to create: We can choose to create client side webpart or an extension. Choose webpart option.
- Selected choice: WebPart
- Web part name: Hit enter to select the default name or type in any other name.
- Selected choice: LocalizeText
- Web part description: Hit enter to select the default description or type in any other value.
- Selected choice: Localize SPFx web part
- Framework to use: Select any JavaScript framework to develop the component. Available choices are (No JavaScript Framework, React, and Knockout)
- Selected choice: React
- Solution Name: Hit enter to have default name (spfx-react- localization in this case) or type in any other name for your solution.
- Yeoman generator will perform scaffolding process to generate the solution. The scaffolding process will take significant amount of time.
-
Once the scaffolding process is completed, lock down the version of project dependencies by running below command.
npm shrinkwrap -
On the command prompt type below command to open the solution in code editor of your choice.
code .
Localization Support
SPFx solution holds localized texts in loc folder. mystrings.d.ts file declares an interface for strings.
declare interface ILocalizeTextWebPartStrings {
PropertyPaneDescription: string;
BasicGroupName: string;
DescriptionFieldLabel: string;
}
declare module 'LocalizeTextWebPartStrings' {
const strings: ILocalizeTextWebPartStrings;
export = strings;
}
By default en-us.js file has localized texts in English. The default locale used by the SharePoint Framework is en-US. To support localization for any language, we need to add js file for each supported language.
Localize web part property pane
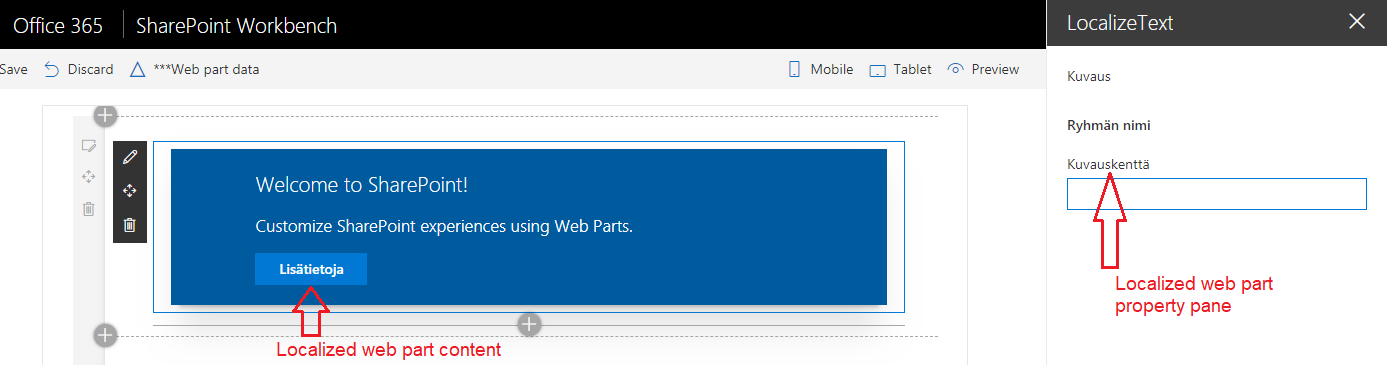
Add file fi-fi.js under “\src\webparts\localizeText\loc" with localization for Finnish language.
define([], function() {
return {
"PropertyPaneDescription": "Kuvaus",
"BasicGroupName": "Ryhmän nimi",
"DescriptionFieldLabel": "Kuvauskenttä"
}
});
Localize web part content
The content inside web part can be localized the same way as of web part property pane. For each of the string to be localized, add key in localization TypeScript definition file and localized values in each of the locale js files.
We will localize the button text of web part.
Step 1: Add key in localization TypeScript definition file
- Open mystrings.d.ts under “\src\webparts\localizeText\loc".
- Add key for button text.
declare interface ILocalizeTextWebPartStrings {
PropertyPaneDescription: string;
BasicGroupName: string;
DescriptionFieldLabel: string;
LearnMoreButtonLabel: string;
}
declare module 'LocalizeTextWebPartStrings' {
const strings: ILocalizeTextWebPartStrings;
export = strings;
}
Step 2: Add localized values in each of the locale js files
Add below content to file at “\src\webparts\localizeText\loc\en-us.js” with localization for English language.
define([], function() {
return {
"PropertyPaneDescription": "Description",
"BasicGroupName": "Group Name",
"DescriptionFieldLabel": "Description Field",
"LearnMoreButtonLabel": "Learn more"
}
});
Add below content to file at “\src\webparts\localizeText\loc\fi-fi.js” with localization for Finnish language.
define([], function() {
return {
"PropertyPaneDescription": "Kuvaus",
"BasicGroupName": "Ryhmän nimi",
"DescriptionFieldLabel": "Kuvauskenttä",
"LearnMoreButtonLabel": "Lisätietoja"
}
});
Step 3: Globalization of web part
- Open “\src\webparts\localizeText\components\LocalizeText.tsx”
-
Add reference to localized strings.
import * as strings from 'LocalizeTextWebPartStrings'; -
Replace the actual content with the references to localized strings.
export default class LocalizeText extends React.Component<ILocalizeTextProps, {}> { public render(): React.ReactElement<ILocalizeTextProps> { return ( <div className={ styles.localizeText }> <div className={ styles.container }> <div className={ styles.row }> <div className={ styles.column }> <span className={ styles.title }>Welcome to SharePoint!</span> <p className={ styles.subTitle }>Customize SharePoint experiences using Web Parts.</p> <p className={ styles.description }>{escape(this.props.description)}</p> <a href="https://aka.ms/spfx" className={ styles.button }> <span className={ styles.label }>{strings.LearnMoreButtonLabel}</span> </a> </div> </div> </div> </div> ); } }
Test web part property pane
The locale value of spPageContextInfo.currentUICultureName is being used as default locale. On SharePoint local workbench default locale used is en-US.
Run gulp serve by specifying the locale parameter:
gulp serve --locale=fi-fi

Summary
Localization helps to build better content for users worldwide. SharePoint Framework supports localization by maintaining localized values in separate JavaScript files per language.
This content was originally posted here.


Leave a comment